Why Learn Git & GitHub?
Track Changes
Keep a complete history of your code, with the ability to revert to any previous version at any time.
Collaborate
Work seamlessly with others on the same project without overwriting each other's changes.
Build Your Portfolio
Showcase your work to potential employers and contribute to open-source projects.
Git Basics
Getting Started with Git
Git is a distributed version control system that helps you track changes to files and coordinate work among multiple people.
1. Installing Git
First, you need to install Git on your computer:
- Windows: Download from git-scm.com
- Mac: Install with Homebrew using
brew install gitor download from git-scm.com - Linux: Use your package manager, e.g.,
sudo apt-get install git
2. Configuring Git
After installation, set up your identity:
Creating Your First Repository
A repository (or "repo") is a project that Git tracks. Let's create one:
git init command creates a hidden .git directory that stores all the version history for your project.
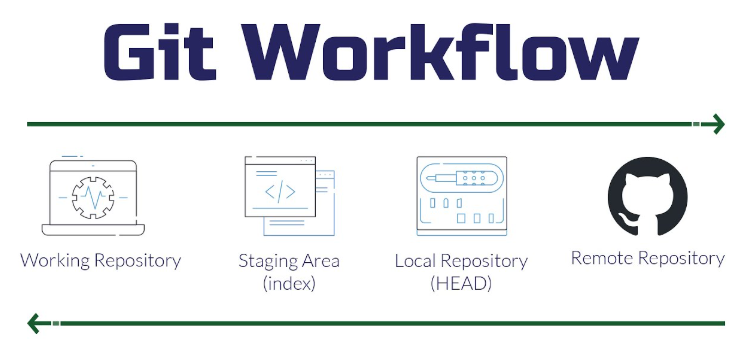
Understanding the Git Workflow
Git has three main states that your files can live in:
- Working Directory: Where you modify files
- Staging Area (Index): Where you mark files ready to be saved
- Repository: Where Git permanently stores changes as commits
Basic Git Commands
Tracking Changes
Viewing History
GitHub Essentials
What is GitHub?
GitHub is a web-based hosting service for Git repositories. It adds many collaboration features on top of Git, including:
- Issues and pull requests for project management
- Code review tools
- Project wikis and websites
- Social coding features
Creating a GitHub Account
Visit github.com and sign up for a free account. Students can get additional benefits through the GitHub Student Developer Pack.
Connecting to GitHub
To connect your local Git repository to GitHub:
1. Create a new repository on GitHub
Go to GitHub, click the "+" icon in the top right, and select "New repository".
2. Connect your local repository
git push -u origin master instead.
GitHub Workflow
Once your repository is on GitHub, follow this workflow to make changes:
Collaborating with Others
Branching Strategy
Branches allow you to develop features isolated from each other. Here's a typical workflow:
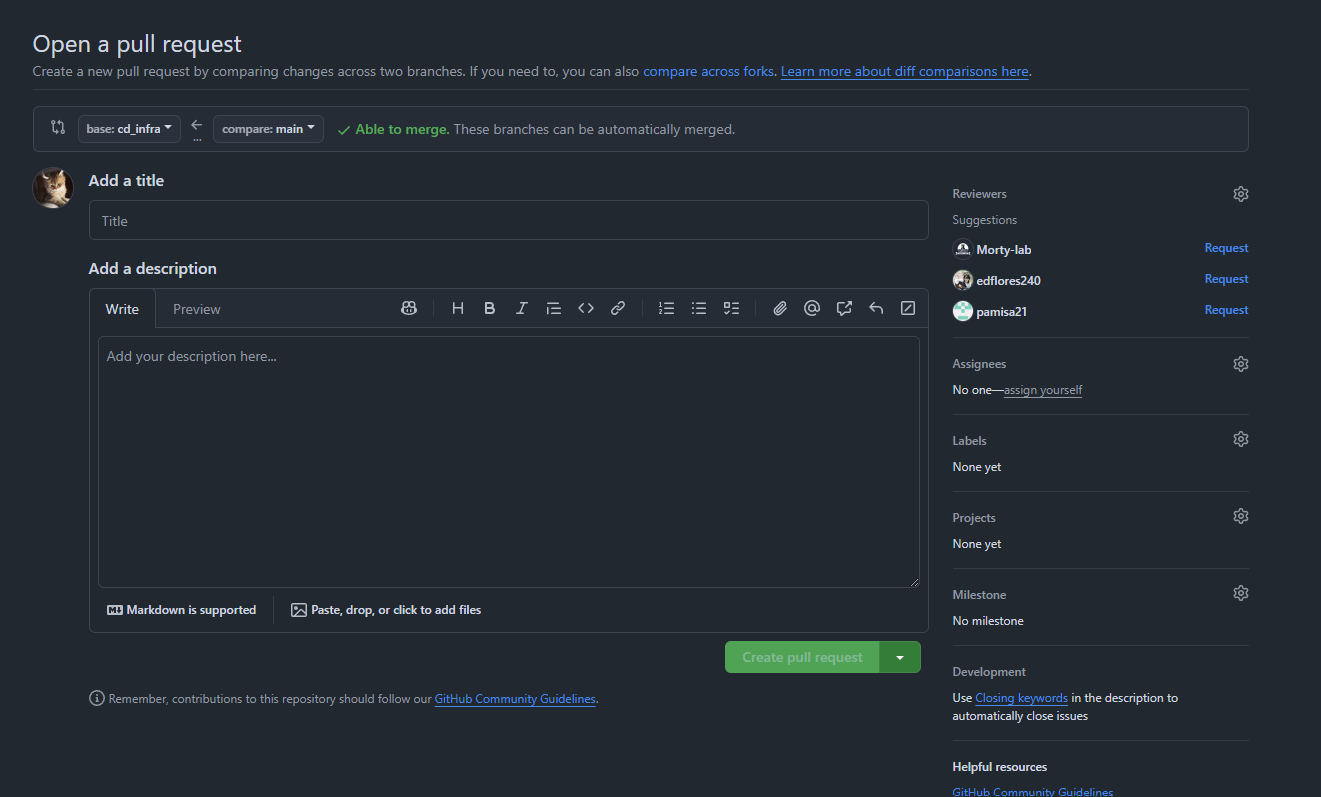
Pull Requests
Pull requests are GitHub's way to propose changes to a repository:
- Push your branch to GitHub
- Go to the repository on GitHub
- Click "Compare & pull request"
- Add a title and description
- Click "Create pull request"
Code Reviews
Code reviews help maintain code quality and share knowledge:
- Reviewers can comment on specific lines of code
- Discuss implementation details and alternatives
- Approve or request changes to the pull request
Handling Merge Conflicts
Merge conflicts occur when Git can't automatically merge changes:
Advanced Git & GitHub Techniques
GitHub Actions (CI/CD)
GitHub Actions allows you to automate workflows like testing and deployment directly from your repository.
GitHub Pages
Host websites directly from your GitHub repository. Great for portfolios, documentation, and project websites.